Quality Products
At a Fair Price
Wholesale Provider
Of Valves & Fittings
- HOME
- Products
- Ball Valves
- Bull Plugs & Swages
- Butterfly Valves
- Check Valves
- Cushion / Flow Tees & Bleed Rings
- Enhanced Oil Recovery
- Floating Ball Valves
- Foot Valves
- Forged Steel Fittings
- Forged Steel Outlets
- Gaskets-Insulation Kits
- Gate Valves
- Gate, Globe & Check Valves
- Malleable Fittings
- Needle Valves
- Nipples
- Piston Valves
- Plug Valves
- Stainless Steel Flanges, Fittings & Nipples
- Strainers
- Studs
- Trunnion
- Unions
- Weld Fittings & Flanges
- Manufacturers
- Advance
- American Block
- Anvil
- Balon
- Bonney Forge
- Champion
- Clayton Mark
- Crane
- Daniel
- DMIC
- GMI
- Galli & Cassina
- Hackney-Ladish
- JMC
- Lone Star
- MATCO
- Marpac-McCanna
- National Flange
- National Gasket
- Nordstrom
- Nutron
- PPI
- SHARPE
- SMI
- TEXSTEAM
- TEX-THREAD
- Titan
- USA Fastner
- Vogt
- Weld Bend
- Westbrook
- Wheatley
- Williams
- WKM
- Wolar
- Locations
- Contact
- Blog
- Careers
- Get a Quote
- HOME
- Products
- Ball Valves
- Bull Plugs & Swages
- Butterfly Valves
- Check Valves
- Cushion / Flow Tees & Bleed Rings
- Enhanced Oil Recovery
- Floating Ball Valves
- Foot Valves
- Forged Steel Fittings
- Forged Steel Outlets
- Gaskets-Insulation Kits
- Gate Valves
- Gate, Globe & Check Valves
- Malleable Fittings
- Needle Valves
- Nipples
- Piston Valves
- Plug Valves
- Stainless Steel Flanges, Fittings & Nipples
- Strainers
- Studs
- Trunnion
- Unions
- Weld Fittings & Flanges
- Manufacturers
- Advance
- American Block
- Anvil
- Balon
- Bonney Forge
- Champion
- Clayton Mark
- Crane
- Daniel
- DMIC
- GMI
- Galli & Cassina
- Hackney-Ladish
- JMC
- Lone Star
- MATCO
- Marpac-McCanna
- National Flange
- National Gasket
- Nordstrom
- Nutron
- PPI
- SHARPE
- SMI
- TEXSTEAM
- TEX-THREAD
- Titan
- USA Fastner
- Vogt
- Weld Bend
- Westbrook
- Wheatley
- Williams
- WKM
- Wolar
- Locations
- Contact
- About
- Careers
- Get a Quote
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does it Work?
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is a critical innovation in orthopedic surgery. This device provides stability to fractures of the tibia, allowing for effective healing. Recent studies estimate that the use of interlocking nails has increased by over 30% in the last five years due to their reliability and success in reducing recovery time.
Dr. John Smith, an expert in orthopedic surgery, states, “The Tibial Interlocking Nail represents a turning point in how we treat complex fractures.” He emphasizes the importance of advancements in surgical techniques. However, challenges still exist in patient-specific applications. Not all cases respond ideally to this method, requiring surgeons to carefully assess each situation.
The design of the Tibial Interlocking Nail allows for enhanced load distribution, yet not every patient may achieve the desired outcomes. Surgeons often reflect on the need for a personalized approach. This highlights the ongoing evolution and the necessity for continued research in this field. The journey of improvement is ongoing, urging both professionals and patients to remain hopeful yet pragmatic.
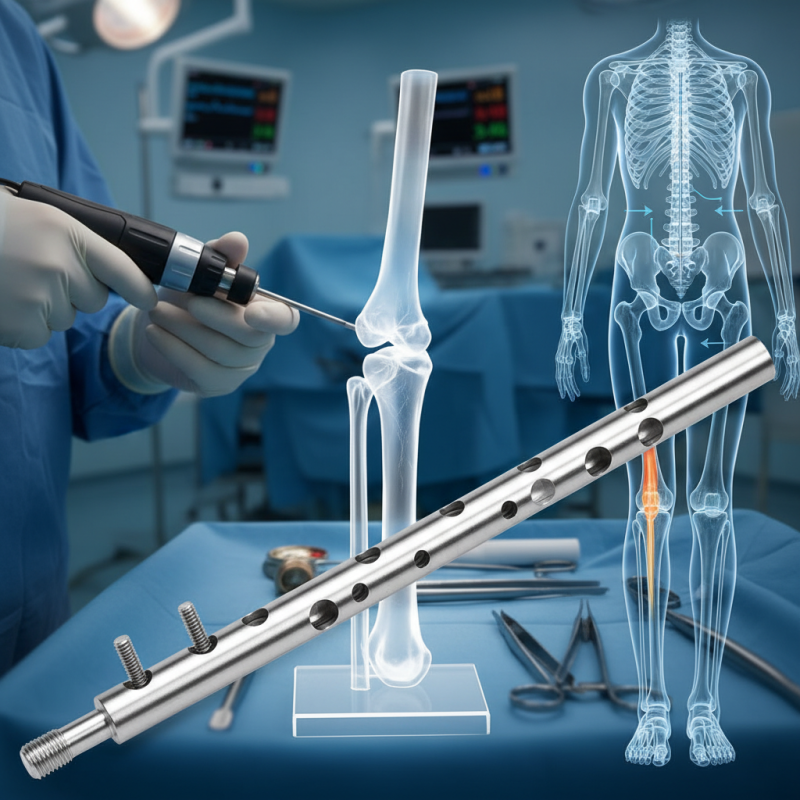
Definition and Purpose of Tibial Interlocking Nail
A Tibial Interlocking Nail is a medical device used in orthopedic surgery. It provides stabilization for fractured tibias. This device is typically made of stainless steel or titanium. It has a long nail that is inserted into the medullary canal of the tibia. The interlocking mechanism helps secure the nail in place.
The primary purpose of a Tibial Interlocking Nail is to facilitate healing. It offers strong support to the fractured bone. Surgeons use this method to reduce complications during the healing process. Patients can often bear weight sooner than with traditional casting. This technique can improve overall recovery time.
Tips: Proper post-operative care is essential. Follow your surgeon's instructions closely. Engage in physical therapy as advised. This can enhance your recovery further. Always report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. Small issues can sometimes lead to bigger problems. Remember, achieving full mobility can take time and patience.
Mechanism of Action: How Tibial Interlocking Nails Work
Tibial interlocking nails are essential in treating certain bone fractures. They provide internal support for the tibia, improving stabilization. The mechanism involves inserting a long metal rod into the bone. This rod is locked in place with screws at both ends. This locking system prevents movement, allowing for proper healing.
When a fracture occurs, the tibial interlocking nail holds the bone fragments together. This method secures the alignment of the bone. It can facilitate faster recovery. The nails can also be removed later, once healing is stable. However, surgery carries risks. Infections and complications can arise.
**Tips:** Ensure you follow post-operative instructions carefully. Regular check-ups help monitor healing progress. If you experience unusual pain, contact your healthcare provider promptly. Remember, each body heals differently, so patience is crucial.
Indications for Use in Orthopedic Surgery
Tibial interlocking nails play a crucial role in orthopedic surgery. They are primarily indicated for the treatment of fractures in the tibia, especially when there's a high risk of instability. According to a study from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, the use of interlocking nails significantly reduces the time needed for rehabilitation compared to traditional fixation methods. In cases of complex fractures, this technique can be particularly effective.
Additionally, tibial interlocking nails are beneficial for patients with open fractures or those with soft tissue injuries. A report from the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma notes that these nails offer enhanced stability, allowing for earlier weight-bearing. However, complications can arise. For example, malalignment may occur in about 10% of cases. Proper surgical technique is vital to minimize such risks.
These nails are also indicated in situations where external fixation is not preferred. They enable direct intramedullary fixation, which can decrease the risk of infection. Yet, patient factors such as age and comorbidities can affect outcomes. Studies indicate that in elderly patients, the risk of complications increases by 15% when using this method. Understanding these variables is critical for orthopedic surgeons in order to optimize patient outcomes.
Surgical Procedure for Inserting a Tibial Interlocking Nail
Inserting a tibial interlocking nail is a complex procedure aimed at stabilizing fractured tibias. The surgeon starts with a careful examination of the bone alignment. Anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is comfortable throughout the surgery. The incision is made along the leg to access the tibia directly. Next, the surgeon drills into the bone to prepare for the nail insertion.
The nail is then inserted through a guide. This requires precision and steady hands. Once the nail is in place, locking screws are added. These screws secure the nail to the bone, enhancing stability. Surgeons often face challenges during this step. Misalignment can lead to complications. Thus, careful adjustments are essential.
Post-surgery, monitoring is crucial. Patients may need physical therapy to regain strength. Recovery times vary, influenced by the severity of the fracture. Each case presents unique challenges, making experience vital for surgeons. The goal is a successful healing process, restoring the patient’s mobility.
Postoperative Care and Recovery Considerations
After a tibial interlocking nail surgery, postoperative care is crucial for successful recovery. Patients often experience pain and swelling in the initial days. Ice packs can help reduce swelling, while prescribed medications manage pain. It’s important to follow the dosage instructions carefully. Elevating the leg aids circulation and helps alleviate discomfort.
As recovery progresses, gentle range-of-motion exercises are essential. These exercises prevent stiffness and promote healing. Physical therapy may be recommended, focusing on strengthening the leg gradually. Patients should be prepared for ups and downs. Some days will be better than others, and this fluctuation can be discouraging.
Regular follow-ups with the healthcare provider are important. They monitor the healing process and adjust treatment as necessary. Patients may have questions about their recovery timeline. Clear communication with the medical team helps ease concerns. It’s natural to have doubts and seek reassurance throughout the journey to full recovery.
